

Understanding context: Understanding the parts of speech can help learners interpret the meaning of sentences by providing context. Similarly, using conjunctions and subordinating clauses can help learners create more complex and sophisticated sentences. For example, by using different types of adjectives and adverbs, learners can create more descriptive and interesting sentences.

Improving writing skills: Knowing how to use different parts of speech can help learners add variety and depth to their writing.
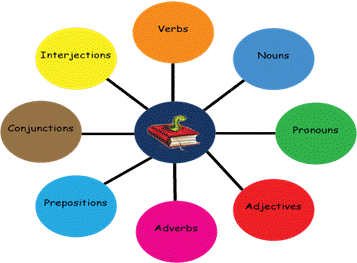
By knowing how to use nouns, verbs, adjectives, and other parts of speech correctly, learners can avoid common errors and produce more accurate and understandable sentences. For example, if a learner knows that "happy" is an adjective, they can recognize that it describes a noun, and use it correctly in a sentence.Ĭreating grammatically correct sentences: A solid understanding of the parts of speech is crucial for constructing grammatically correct sentences. Here are some ways in which knowledge of the parts of speech can be useful in English language learning:īuilding vocabulary: Knowing the parts of speech can help learners identify and understand the meanings of new words. Understanding the parts of speech is essential in learning English grammar and improving one's language skills. Advise students to "write around" the situation by replacing a singular antecedent with a plural one: " All students should bring their own calculators.After learning about basic grammar, one of the most important parts in it is parts of speech. Inventing an indeterminate singular personal pronoun would resolve this issue, but no attempts so far have gained widespread usage. For many years, English speakers have substituted the plural ( they, their) for singular indefinite antecedents: " Everyone should bring their own calculator." In writing, this shift from singular to plural has been considered nonstandard, but using gendered singular pronouns has been considered sexist. Note that relative, indefinite, and interrogative pronouns also have indefinite gender ( who, whose, someone, anyone). Gender of personal pronouns include masculine ( he, his, him), feminine ( she, her, hers), and neuter ( it, its).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
